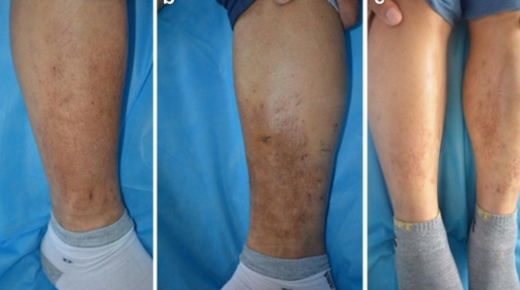
What is Lichen Amyloidosis
Lichen amyloidosis is a chronic skin condition characterized by the accumulation of amyloid deposits in the skin, leading to the development of persistent, itchy papules or plaques. It is considered a subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis (PLCA).
Causes of Lichen Amyloidosis
The exact cause of lichen amyloidosis is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from prolonged friction or scratching of the skin, leading to the deposition of amyloid proteins. Genetic factors may also play a role in predisposing individuals to develop the condition.
Symptoms of Lichen Amyloidosis
The primary symptom of lichen amyloidosis is the presence of small, brownish or reddish papules or plaques on the skin, typically occurring on the shins, thighs, lower legs, or forearms. These lesions may be intensely itchy and can cause discomfort and distress for affected individuals.
Diagnosis of Lichen Amyloidosis
Diagnosing lichen amyloidosis typically involves a thorough physical examination and evaluation of the skin lesions. A skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the presence of amyloid deposits in the skin tissue. Additional tests, such as immunohistochemistry or electron microscopy, may be used to further characterize the amyloid protein.
Treatment Options for Lichen Amyloidosis
Treatment for lichen amyloidosis focuses on relieving symptoms, reducing itchiness, and preventing further deposition of amyloid proteins in the skin. Several treatment options may be considered, depending on the severity of symptoms and individual patient preferences.
Topical Treatments
Topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and itchiness associated with lichen amyloidosis. These medications are applied directly to the affected skin and can help alleviate symptoms in some cases.
Oral Medications
In cases where topical treatments are ineffective, oral medications such as antihistamines or gabapentinoids may be prescribed to help control itching and discomfort. These medications work by blocking histamine receptors or modulating nerve activity to reduce itching sensations.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, including treatments such as narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) therapy or psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy, may be recommended for individuals with severe or widespread lichen amyloidosis. These treatments use controlled exposure to UV light to suppress inflammation and reduce itchiness.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves the application of extreme cold to the skin lesions using liquid nitrogen. This treatment may help reduce the size and thickness of amyloid deposits in the skin, leading to improvement in symptoms and appearance.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy, such as pulsed dye laser or fractional laser resurfacing, may be considered for individuals with refractory lichen amyloidosis. These treatments target the abnormal blood vessels and tissue structures associated with amyloid deposits, leading to a reduction in symptoms and improved skin texture.
Patient Education and Support
In addition to medical treatments, patient education and support are essential components of managing lichen amyloidosis. Healthcare providers can educate patients about proper skin care techniques, including avoiding excessive scratching or friction, moisturizing the skin regularly, and using gentle skincare products.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with a dermatologist or healthcare provider are important for individuals with lichen amyloidosis to assess treatment response, monitor disease progression, and address any complications or concerns that may arise.
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle modifications, such as wearing loose-fitting clothing, avoiding hot showers or baths, and practicing stress-reduction techniques, may help minimize itching and discomfort associated with lichen amyloidosis. Maintaining good overall skin health through proper hygiene and skincare practices is also important.
Surgical Intervention
In rare cases where lichen amyloidosis causes significant cosmetic or functional impairment, surgical intervention may be considered. Procedures such as excision of affected skin lesions or skin grafting may be performed to improve the appearance and texture of the skin.
Conclusion
Lichen amyloidosis is a chronic skin condition characterized by the accumulation of amyloid deposits in the skin, leading to persistent itching and discomfort for affected individuals. While there is no cure for lichen amyloidosis, various treatment options are available to help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. By working closely with healthcare providers and following recommended treatment regimens, individuals with lichen amyloidosis can effectively manage their condition and minimize its impact on daily life.