1. Introduction to Macular Amyloidosis Pigmentation
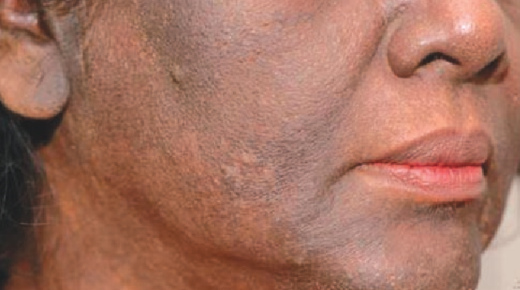
Macular amyloidosis pigmentation is a skin condition characterized by the deposition of amyloid protein in the skin’s dermis, leading to brownish patches or spots on the skin.
2. Causes of Macular Amyloidosis Pigmentation
The exact cause of macular amyloidosis pigmentation is unknown, but it is believed to be associated with genetic factors, sun exposure, friction, and chronic scratching or rubbing of the skin.
3. Symptoms of Macular Amyloidosis Pigmentation
Symptoms of macular amyloidosis pigmentation include the appearance of small, dark brown or gray patches on the skin, typically on the upper back, chest, or arms. These patches may be itchy or asymptomatic.
4. Diagnosis of Macular Amyloidosis Pigmentation
Diagnosis of macular amyloidosis pigmentation is usually based on clinical examination and may be confirmed through skin biopsy, which reveals characteristic amyloid deposits in the dermis.
5. Treatment Options for Macular Amyloidosis Pigmentation
Treatment for macular amyloidosis pigmentation aims to improve the appearance of the skin and alleviate symptoms. Several treatment options are available, including topical medications, laser therapy, and phototherapy.
6. Topical Medications
Topical medications such as corticosteroids or retinoids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and pigmentation in the affected areas of the skin.
7. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy, including pulsed dye laser or fractional laser resurfacing, can help target and reduce the appearance of pigmented patches associated with macular amyloidosis.
8. Phototherapy
Phototherapy, using ultraviolet (UV) light or psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy, may be effective in reducing pigmentation and improving the overall appearance of the skin.
9. Moisturizers and Emollients
Regular use of moisturizers and emollients can help hydrate the skin, improve its texture, and reduce the appearance of pigmented patches associated with macular amyloidosis.
10. Avoidance of Irritants
Avoiding factors that exacerbate macular amyloidosis pigmentation, such as sun exposure, friction, and scratching or rubbing of the skin, can help prevent worsening of symptoms and pigmentation.
11. Gentle Skin Care
Practicing gentle skin care, including using mild cleansers and avoiding harsh chemicals or abrasive exfoliants, can help maintain the skin’s barrier function and minimize irritation in individuals with macular amyloidosis pigmentation.
12. Protection from Sun Exposure
Sun protection, including wearing protective clothing, using broad-spectrum sunscreen, and seeking shade, is essential for individuals with macular amyloidosis pigmentation to prevent further darkening of the skin.
13. Management of Itching
For individuals experiencing itching associated with macular amyloidosis pigmentation, antihistamines or topical corticosteroids may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort and reduce scratching.
14. Monitoring for Complications
Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is important for individuals with macular amyloidosis pigmentation to detect any changes in the skin and monitor for potential complications such as infection or ulceration.
15. Counseling and Support
Counseling and support groups can provide emotional support and guidance for individuals living with macular amyloidosis pigmentation, helping them cope with the psychological impact of the condition.
16. Education on the Condition
Educating individuals with macular amyloidosis pigmentation about their condition, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, empowers them to make informed decisions about their skin care and management.
17. Long-Term Outlook
While macular amyloidosis pigmentation is a chronic condition, with proper treatment and management, many individuals can achieve improvement in the appearance of their skin and reduction in symptoms over time.
18. Research and Advances
Ongoing research into the pathogenesis and treatment of macular amyloidosis pigmentation may lead to the development of new therapeutic approaches and improved outcomes for affected individuals in the future.
19. Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention and treatment of macular amyloidosis pigmentation can help prevent progression of the condition and minimize its impact on the individual’s quality of life.
20. Multidisciplinary Approach to Care
A multidisciplinary approach involving dermatologists, primary care physicians, and other healthcare providers is often necessary for the comprehensive management of macular amyloidosis pigmentation.
21. Patient Advocacy
Patient advocacy organizations play a crucial role in raising awareness about macular amyloidosis pigmentation, advocating for research funding, and providing support and resources for affected individuals and their families.
22. Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
Open communication and collaboration between individuals with macular amyloidosis pigmentation and their healthcare providers are essential for developing personalized treatment plans and achieving optimal outcomes.
23. Addressing Psychosocial Impact
Addressing the psychosocial impact of macular amyloidosis pigmentation, including body image concerns and emotional distress, is an important aspect of comprehensive care for affected individuals.
24. Empowerment Through Knowledge
Empowering individuals with macular amyloidosis pigmentation through knowledge about